Add, subtract, multiply, and divide
key notes :
1️⃣ Addition (+)
Meaning: Joining two or more numbers to get a total.
Example: 23 + 15 = 38
Tips:
- Always start adding from the ones place.
- Carry over if the sum is more than 9.
Emoji hint: 🟢➕🟢 = 🟢🟢
2️⃣ Subtraction (−)
Meaning: Taking away a number from another.
Example: 50 − 27 = 23
Tips:
- Start from the ones place.
- Borrow from the next higher place if needed.
Emoji hint: 🍎−🍏 = 🍎
3️⃣ Multiplication (×)
Meaning: Repeated addition of the same number.
Example: 4 × 3 = 12 (4 + 4 + 4 = 12)
Tips:
- Memorize tables up to 12 × 12.
- Use patterns in tables to multiply quickly.
Emoji hint: 3️⃣×2️⃣ = 6️⃣
4️⃣ Division (÷)
Meaning: Sharing a number equally or finding how many times a number fits into another.
Example: 12 ÷ 3 = 4
Tips:
- The number to be divided = dividend
- The number we divide by = divisor
- The answer = quotient
Emoji hint: 🍰 ÷ 4️⃣ = 🍰🍰🍰🍰
5️⃣ Quick Tricks
Addition & Subtraction: Check by doing the opposite operation.
- Example: 23 + 15 = 38 → 38 − 15 = 23 ✅
Multiplication & Division: Check by doing the opposite operation.
- Example: 4 × 3 = 12 → 12 ÷ 3 = 4 ✅
Learn with an example
Add: 34396 and 58124.
Solution:
Step I: Add the ones. 6 + 4 = 10 ones = 1 ten and 0 one. Write 0 in one’s column and carry 1 to the tens column.
Step II: Add the tens. 9 + 2 + 1 (carry over) = 12 tens. 12 tens = 1 hundreds and 2 tens. Write 2 in the tens column and carry 1 to the hundreds column.
Step III: Add the hundreds. 3 + 1 + 1 (carry over) = 5 hundreds. Write 5 in the hundreds column.
Step IV: Add the thousands column. 4 + 8 = 12 thousands. 12 thousands = 1 ten thousand and 2 thousands. Write 2 in the thousands column.
Step V: Add the ten thousand column. 3 + 5 + 1 (carry over) = 9 ten thousands. Write 9 in ten thousand columns.
Adding 5-digit Numbers with Regrouping
Hence, 34396 + 58124 = 92520
| 1 11 |
| 34396 |
| 58124 |
| 92,520 |
📗Multiply.
95 x 7=___________
- Multiply the ones. Remember to carry over.
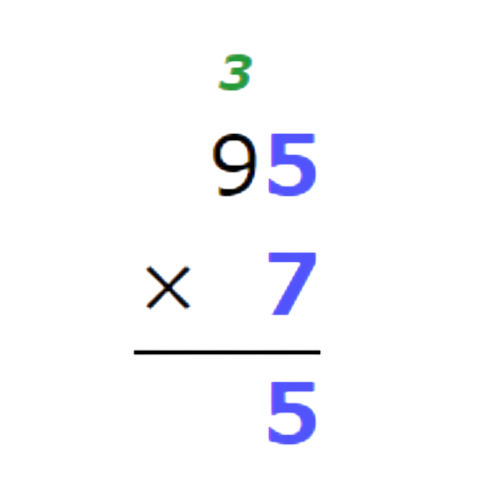
- Multiply the tens. Multiply 9 times 7, then add 3.
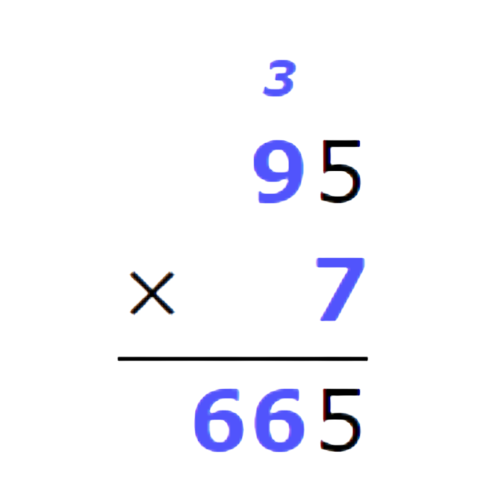
- The product is 665.
📗 Multiply.
314 x 2=_____
- Multiply the ones.
- 314 x 2 =8
- Multiply the tens.
- 314 x 2 = 28
- Multiply the hundreds.
- 314 x 2 = 628
- The product is 628.
📗 Subtract.
798-721=____
- Subtract the ones. Subtract 8–1.
- 798-721=1
- Subtract the tens. Subtract 9–2.
- 798-721=77
- Subtract the hundreds. Subtract 7–7.
- 798-721=077
- The difference is 77.
🥏 Dividing a 3-digit number by a 1-digit number
You can use long division to divide larger numbers, too. Follow the steps below to divide a 3-digit number by a 1-digit number. Try it with 769÷3.
Write the problem using a long division symbol.
To divide, start with the digit in the hundreds place. Find how many times 3 goes into 7.
It goes in 2 times. Write the 2 above the 7. Multiply 3×2=6. Write the 6 below the 7. Subtract 7–6=1. There is 1 left over. Next, bring the 6 down from the tens place to make the number 16. Find how many times 3 goes into 16.
It goes in 5 times. Write the 5 above the 6. Multiply 3×5=15. Write the 15 below the 16. Subtract 16–15=1. There is 1 left over. Then, bring down the 9 from the ones place to make the number 19. How many times does 3 go into 19?
It goes in 6 times.Write the 6 above the 9.Multiply 3×6=18. Write the 18 below the 19.Subtract 19–18=1.There is 1 left over.We have 1 left over. There are no more digits to divide, so 1 is a remainder. That means 3 doesn’t go into 769 evenly. We write the remainder as R1.
So, 769÷3=256 R1!
Let’s practice!🖊️

