The Earth’s Water
key notes :
Water Distribution on Earth:

- About 71% of the Earth’s surface is covered by water.
- Most of Earth’s water is in oceans (about 97%).
- Only 3% of Earth’s water is freshwater, and most of it is trapped in ice caps and glaciers.
Types of Water:
- Saltwater: Found in oceans and seas, and is not suitable for drinking.
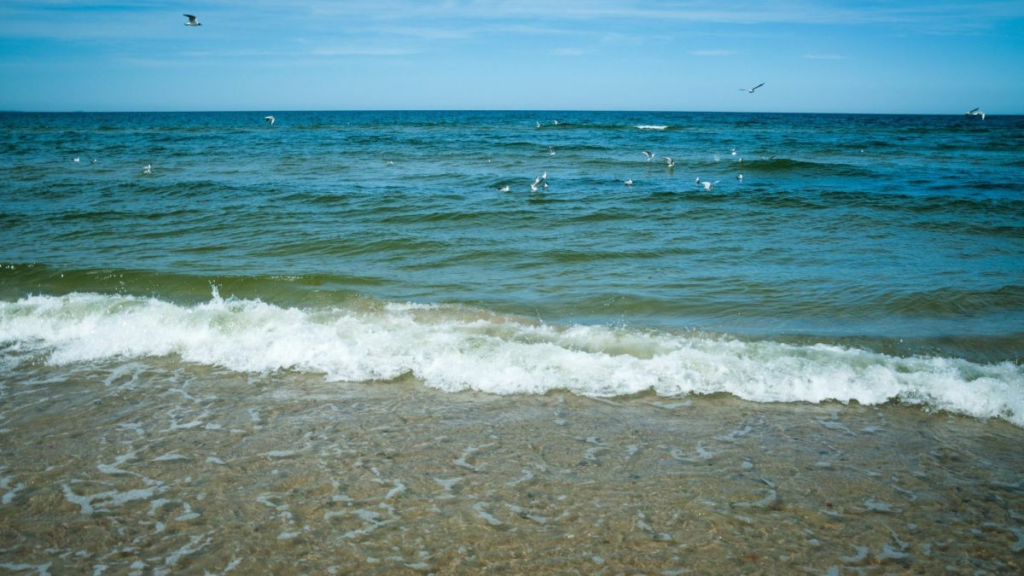

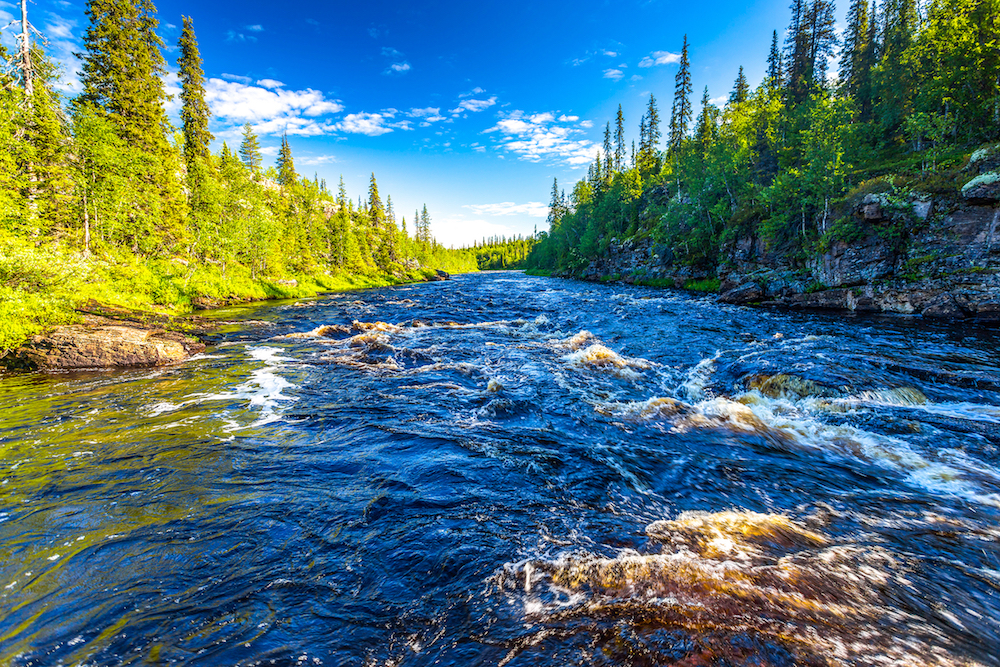
- Freshwater: Found in rivers, lakes, and groundwater. It is used for drinking, agriculture, and daily needs.

Water Cycle:
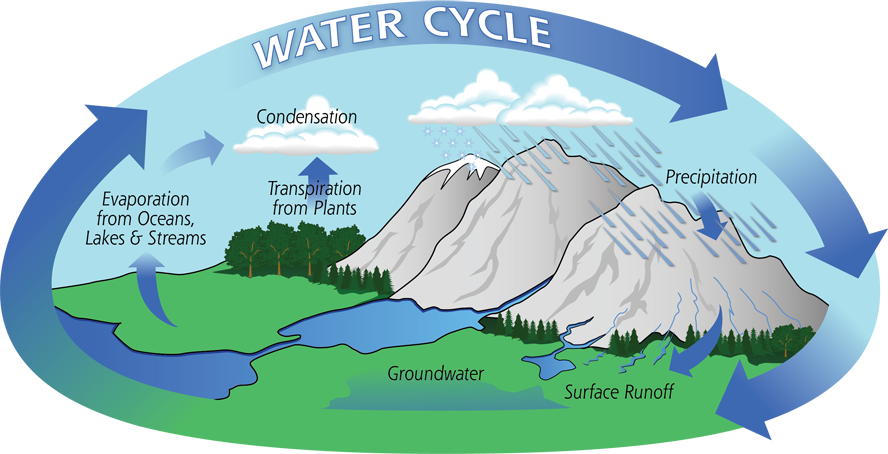
- Evaporation: Water from oceans, rivers, and lakes turns into vapor and rises into the atmosphere.
- Condensation: Water vapor cools down and forms clouds.
- Precipitation: Water falls back to Earth in the form of rain, snow, or hail.
- Collection: Water collects in oceans, rivers, lakes, and underground reservoirs.
Importance of Water:
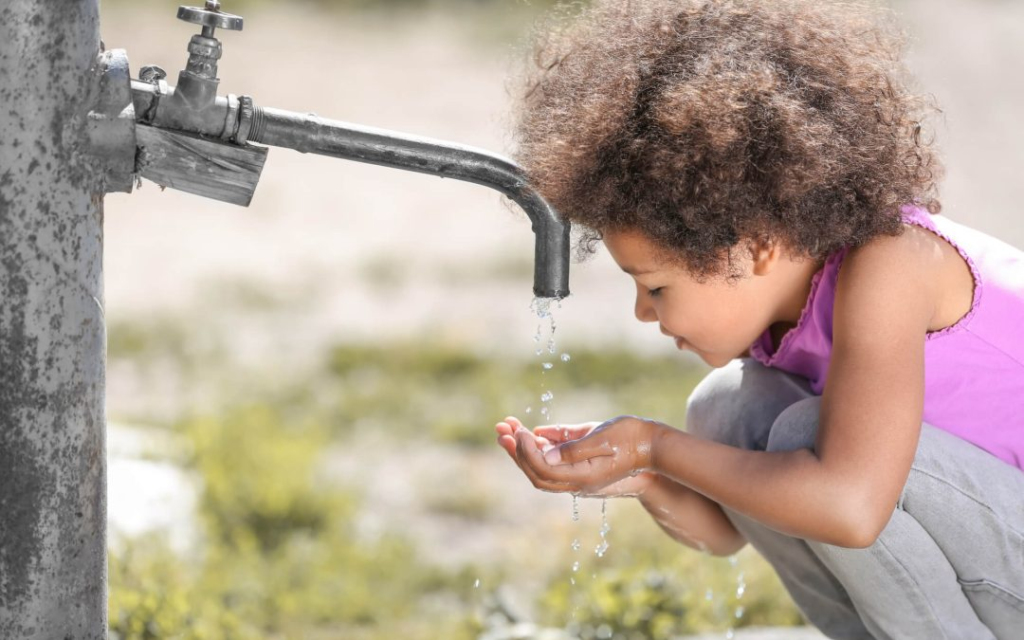
- Supports life: Water is essential for all living organisms, including humans, animals, and plants.

- Agriculture: Plants need water for growth, and it is used to irrigate crops.
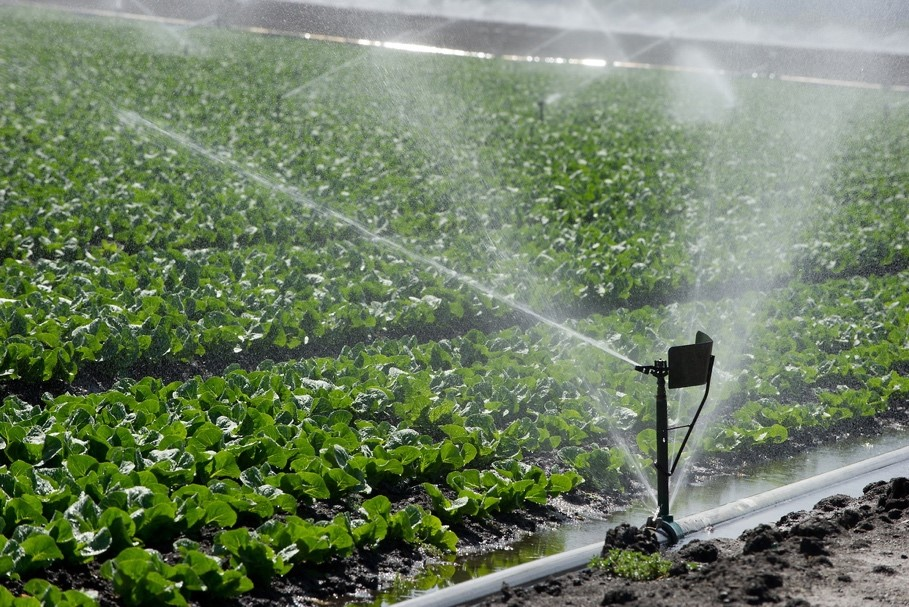

- Drinking water: Humans need freshwater for drinking and sanitation.
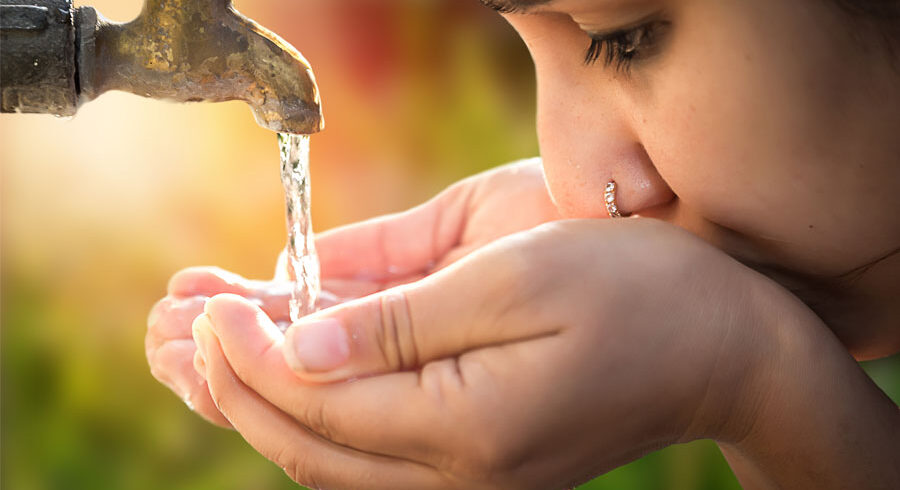

Conservation of Water:
- Water is a limited resource, so it’s important to use it wisely.
- Simple actions like turning off taps when not in use, fixing leaks, and using less water in daily activities can help conserve it.
Let’s practice!

