Revolution Of The Earth Causes The Seasons
key notes :
Definition of Revolution:
- The Earth revolves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit.
- One complete revolution takes 365 1/4 days, which equals one year.
Tilt of the Earth’s Axis:

- The Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees.
- This tilt is the main reason why different parts of the Earth experience different seasons.
Position of the Earth and Seasons:

- As the Earth moves around the Sun, different areas receive varying amounts of sunlight, leading to the seasons.
- Summer: When a hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, it experiences summer.
- Winter: When a hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, it experiences winter.
- Spring and Autumn: These are transition periods when neither hemisphere is tilted significantly toward or away from the Sun.
Effect of Sunlight:
- During summer, the Sun appears higher in the sky, and days are longer because the Sun’s rays are more direct.
- During winter, the Sun is lower in the sky, and days are shorter because the rays are less direct.
Solstices and Equinoxes:
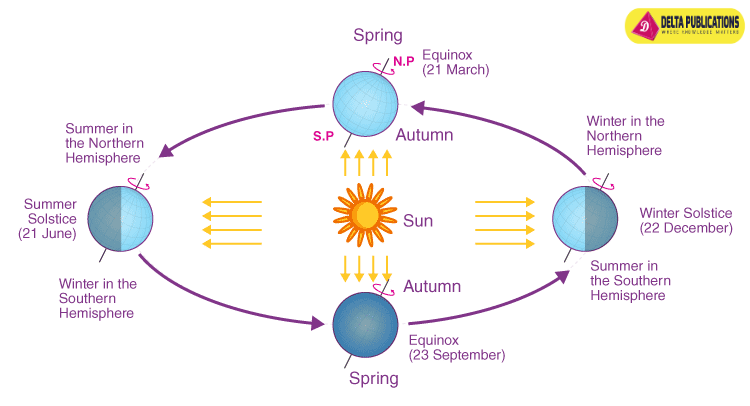
- Summer Solstice: The longest day of the year (around June 21).
- Winter Solstice: The shortest day of the year (around December 21).
- Equinoxes: Equal day and night (around March 21 and September 23).
Difference Between Rotation and Revolution:

- Rotation: The Earth spins on its axis, causing day and night.
- Revolution: The Earth moves around the Sun, causing seasons.
Importance of Seasons:
- Seasons affect weather, plant growth, and human activities.
- They bring variety to the environment and play a key role in the life cycles of living organisms.
Let’s practice!

