The States Of Matter
key notes :
What is Matter?
- Matter is anything that has weight and takes up space.
- Examples: Water, air, rocks, and your body are all types of matter.
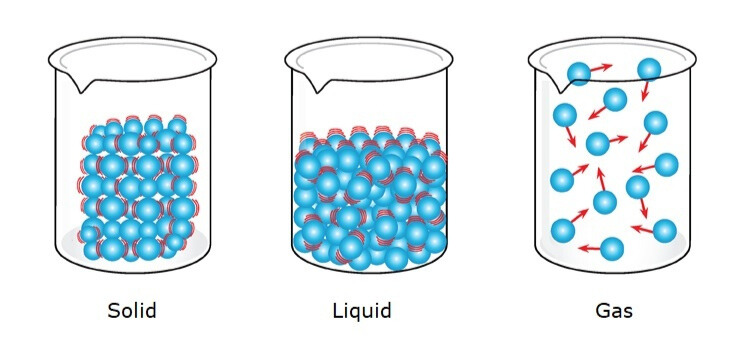
Three States of Matter:
Solid: Has a fixed shape and volume.
- Example: Ice, rocks, or a chair.

Liquid: Has a fixed volume but takes the shape of its container.
- Example: Water, milk, or juice.

Gas: Has no fixed shape or volume and spreads to fill the container.
- Example: Air, steam, or helium.

Properties of States of Matter:

- Solids are hard and cannot be easily compressed.
- Liquids flow and can be poured.
- Gases are invisible and spread out freely.
Changes in States of Matter:
- Melting: Solids turn into liquids (e.g., ice melting into water).

- Freezing: Liquids turn into solids (e.g., water freezing into ice).

- Evaporation: Liquids turn into gases (e.g., water turning into steam).

- Condensation: Gases turn into liquids (e.g., steam cooling to water).

Importance of States of Matter:
- Solids are used to make buildings and tools.
- Liquids are essential for drinking and cooking.
- Gases are important for breathing and inflating balloons.
Fun Facts:
- Water is the only substance that naturally exists in all three states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (steam).
- The state of matter can change with temperature and pressure.
Activities to Understand States of Matter:
- Observe melting ice.
- Boil water to see steam (gas) form.
- Cool steam on a lid to see condensation.
Let’s practice!

