Biodegradable And Non-Biodegradable Waste
key notes :
Definition of Waste:
Waste is anything that is no longer needed and is discarded. It can be in the form of food, paper, plastic, or other materials.
Types of Waste:

Waste is classified into two types:
- Biodegradable Waste: Waste that can break down naturally by microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) into simpler substances.
- Non-Biodegradable Waste: Waste that does not break down easily and remains in the environment for a long time.
Examples of Biodegradable Waste:
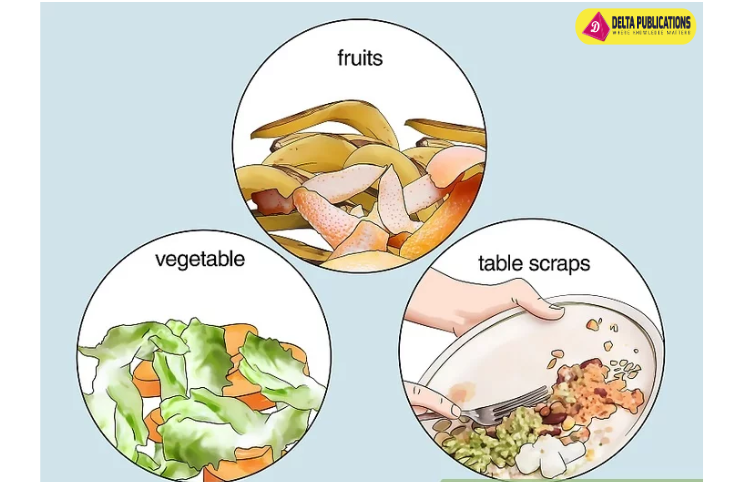
- Food scraps (vegetable peels, fruit peels)
- Paper and cardboard
- Garden waste (leaves, flowers, grass)
- Animal waste
Examples of Non-Biodegradable Waste:

- Plastic bags and bottles
- Metal cans
- Glass
- Styrofoam
Environmental Impact:
- Biodegradable Waste: Can enrich the soil and is eco-friendly if managed properly, such as composting.
- Non-Biodegradable Waste: Pollutes the environment, takes hundreds of years to decompose, and can harm animals and humans.
Proper Waste Disposal:
- Segregation: Separate biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste in different bins.

- Recycling: Reuse or recycle non-biodegradable materials like plastic, metal, and glass.

- Composting: Turn biodegradable waste into compost for plants.

Reduce, Reuse, Recycle (3Rs):

- Reduce: Use less material to minimize waste.
- Reuse: Find new ways to use old items.
- Recycle: Convert waste into reusable materials.
Why It’s Important to Manage Waste:
- Protects the environment from pollution.
- Saves natural resources.
- Keeps surroundings clean and healthy.
Let’s practice!

